


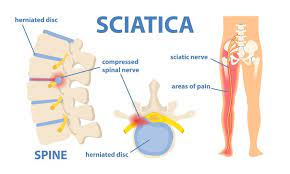
LUMBAGO SCIATICA SYNDROME/ Intervertebral Disc Prolapse (IVDP).
• Lumbago is acute low backache.
• Sciatica is the neuralgic pain that starts in the back and radiates along the posterior aspect of lower limb to heel.
Causes
• Combination of lumbago with sciatica is invariably due to acute intervertebral disc protrusion in the lumbar region (L3-L4; L4-L5; L5-S l ).
• Other rare causes are the following:
• Metastasis
• Tumours
• Tuberculosis of spine
• Spinal canal stenosis
Clinical Features of lntervertebral Disc Prolapse (IVDP)
Lumbago
• Lumbago is localised low backache in the midline that increases on movements of spine or straining (like coughing, sneezing, etc.). There is associated paraspinal muscular spasm.
• Pain starts acutely, usually while attempting to lift weight in bent posture. Lumbago may or may not be associated with sciatica.
Sciatica
• Also known as lumbar radicular pain.
• Occurs due to irritation of a spinal root compressed by the protruded disc close to the intervertebral foramen.
• Pain is shooting, burning or shock-like in character. It maybe continuous or brought on by spinal movements and straining.
• Patient prefers to lie down on his sides with flexed lower limbs.
• Syndrome of pain may or may not be associated with symptoms of neurological deficit, which depends on the root involved.
• L4 root Weakness of invertors of foot, sensory impairment at L4 dermatome (inner aspect of leg) and depressed knee jerk
• LS root Weakness of extensor hallucis longus with sensory impairment at LS dermatome (outer aspect of leg and dorsum of foot)
• S1 root Weakness of plantar flexors of toes, foot and hamstrings with depressed ankle jerk and sensory impairment at S1 dermatome (outer aspect of foot)
• Positive straight leg raising (SLR) test is present.
• Large disc protrusions may cause bilateral, more extensive neurological deficit (cauda equina syndrome)
Investigations
• Plain radiograph of lumbosacral spine:
• Loss of lumbar lordosis
• Scoliosis
• Reduced intervertebral disc space
• On most occasions, radiograph is normal
• CT scan shows the protruded disc. MRI is more sensitive and specific.
Management
• Bed rest for 1-3 weeks; however, presently early return to daily activities is encouraged.
TREATMENT AT DR. SOHAN LAL CLINIC
The integrated POLYCLINIC facility offers patients to select their treatment either from the Department of Homeopathy or from the Department of Medicine.
We provide scientific, research-based, and professional services to people across the world, aiming to achieve the highest success rate.
