


Definition
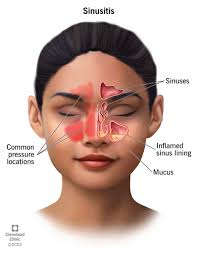
This is chronic inflammatory process affecting the mucosa of various groups of paranasal sinuses.
Aetiology
1. Follows repeated attacks of acute sinusitis and upper and lower respiratory infection.
2. Nasal obstruction leads to chronic sinus infection, eg (a) Deviated nasal septum. (b) Oedematous turbinates. (c) Polyps.
3. Inadequate aeration of the sinuses due to allergy and narrowing of the sinus ostium from infection.
4. Poor nutrition, atmospheric pollution and damp environment.
5. Chronic dental sepsis.
Pathology
Mucosa may show hypertrophic, atrophic or papillary changes.
Two main categories of chronic sinusitis are-
1. Chronic infective sinusitis.
2. Sinusitis as part of generalised respiratory allergy.
Clinical features
Symptoms are variable.
1. Nasal obstruction due to oedema or turgescence of the turbinates.
2. Pain is not a typical feature, but dull ache may be present over the sinus concerned.
3. Headache may present certain periodicity increasing after rising in the morning, but gradually decreasing as the day goes on or vice – versa.
4. Hawking and clearing of throat due to post - nasal discharge. Sometimes patient complains of foul smell or poor sense of smell and taste. Foul smelling discharge is often present, which may be blood stained at times.
5. General feeling of depression, tiredness, and apathy. Low grade pyrexia may be present.
6. Anterior rhinoscopy will reveal dull colour of nasal mucosa. Trickle of pus is seen under the middle meatus, if the anterior group of sinuses are involved. The anterior end of the middle turbinate may be oedematous and turgescent. In such case application of 4 % xylocaine will reduce the swelling and trickle of pus will be seen better.
7. Posterior rhinoscopy will show pus in the middle meatus in maxillary sinusitis and in the spheno - ethmoidal recess in sphenoidal sinusitis.
Radiology of paranasal sinuses (O.M. view) shows some of the following features (a) Mucosal thickening of the lining mucosa; (b) opacity or uniform haziness of the maxillary sinus;( c) polypoid hypertrophy of lining mucosa; (d) fluid level; or (e) osteitis or osteosclerosis.
Nasal swab shows increased eosinophil on smear in allergic variety. Bacteriology shows streptococcus commonly and also pneumococci.
Sinoscopy- fibre - optic sinoscope is introduced in maxillary cavity through antrostomy and detailed pathology seen.
Treatment
Principles in the treatment of chronic paranasal sinus infection should be
1. To encourage ciliary activity.
2. Aeration of the sinus cavity.
3. Adequate drainage.
Conservative Management
1- Aggravating factors such as dust, alcohol and tobacco should be avoided. Dry climate holiday, if possible, is helpful.
2- Nutritious diet and regular diet habits are helpful.
3- Dental treatment if carious teeth or other sepsis.
4- Nasal decongestants help to reduce oedema and open up sinus ostium. 1 % Ephedrine in saline is the ideal decongestant. This helps ciliary activity.
5- Irrigation of the nose with normal saline often helps.
6- Displacement therapy of Proetz with 1 / 2 % Ephedrine in normal saline is often helpful, where change in sinus lining has not progressed too much.
7- Control of infection.
TREATMENT AT DR. SOHAN LAL CLINIC
The integrated POLYCLINIC facility offers patients to select their treatment either from the Department of Homeopathy or from the Department of Medicine.
We provide scientific, research-based, and professional services to people across the world, aiming to achieve the highest success rate.
