



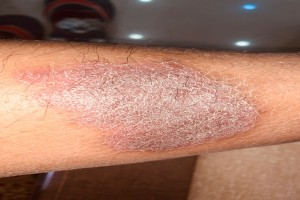
PSORIASIS INDRODUCTION • The main abnormality in psoriasis is the increased epidermal proliferation due to excessive division of cells in the stra
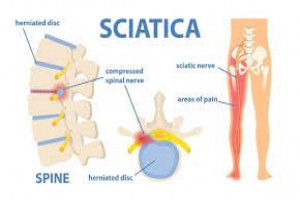
LUMBAGO SCIATICA SYNDROME/ Intervertebral Disc Prolapse (IVDP). • Lumbago is acute low backache. • Sciatica is the neuralgic pain that starts in the

VITILIGO INTRODUCTION • Occurs due to selective destruction of the skin melanocytes that results in development of unsightly depigmented patches. •
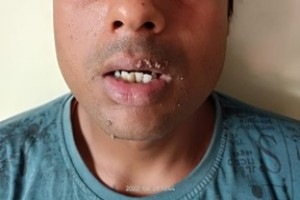
WARTS INTRODUCTION • Warts are the cutaneous manifestations of human papillomavirus (HPV). • Warts may exist in different forms: • Common war
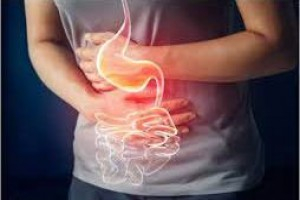
ACID PEPTIC DISEASE OR PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE • Peptic ulcer refers to an ulcer in the lower oesophagus, stomach or duodenum, in the jejunum after surg
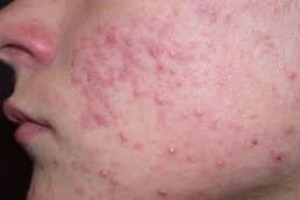
ACNE VULGARIS INTRODUCTION • This is a disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of blocked pilosebaceous follicles. It predominantly affects t

ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS/ RHEUMATOID SPONDYLITIS • Ankylosing spondylitis is a seronegative chronic inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the a

BRONCHIAL ASTHMA DEFINATION • Bronchial asthma is a heterogeneous disease, usually characterised by chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. I
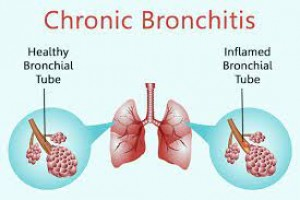
CHRONIC BRONCHITIS DEFINITION • Chronic bronchitis is defined as a condition associated with excessive tracheobronchial mucus production to cause
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS/ SPONDYLITIS • Spondylitis suggests inflammation of intervertebral joints. However, the term commonly refers to degenerative dis
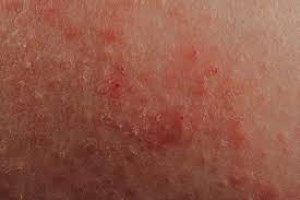
DERMATITIS ECZEMA INTRODUCTION • The terms eczema and dermatitis are used synonymously. Eczema is not a specific disease entity but a characteristic
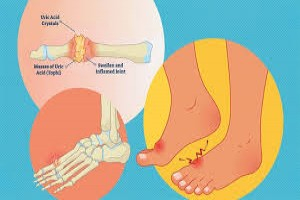
GOUT Aetiology of Gout and Hyperuricaemia 1-Increased production of uric acid 2-Decreased renal excretion of uric acid • Renal failure • Lead pois
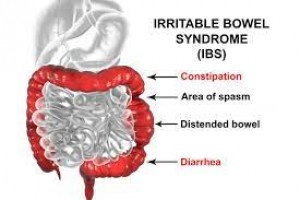
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME • Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a benign, chronic symptom complex of altered bowel habits and abdominal pain. Aetiology
MIGRAINE • Migraine is characterised by periodic headaches, typically unilateral, often associated with visual disturbance and vomiting. Precipitati

EPILEPSY Definition of Epilepsy. • Brief recurrent disorder of cerebral function that is usually associated with disturbance of consciousness and ac

Melasma (also known as chloasma) is a tan or dark skin discoloration. Melasma is thought to be caused by sun exposure, genetic predisposition, hormone
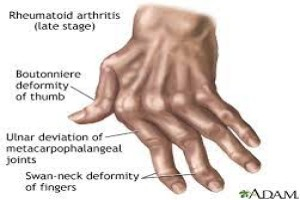
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Introduction • RA is a chronic inflammatory joint disease with multisystem involvement. • Females are affected three times mor
CONSTIPATION • Constipation-patients having bowel movements less frequently than three times a week. If stool is hard and difficult to pass, patient

Introduction Nasal polyps are hypertrophied oedematous mucosa of the nose and paranasal sinuses resulting in a pedunculated mass. This is not a new g
URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) • UTI may be anatomically subdivided into lower tract infections (urethritis, prostatitis and cystitis) and upper tract

• The term obesity implies excess of adipose tissue measured by the following- • Body mass index (BMI). It is defined as person's weight (kg) divided

Types of Viral Hepatitis • Hepatitis A, caused by hepatitis A virus (HAV) • Hepatitis B, caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) • Delta hepatitis, cause
Defination • Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a clinical syndrome characterised by hyperglycaemia due to absolute or relative deficiency of insulin, or both

Introduction • Male sexual dysfunction is termed impotence. It may manifest in various ways like loss of desire, inability to obtain and maintain ere
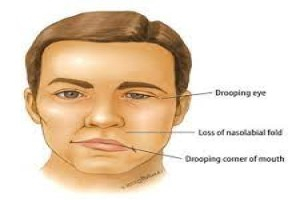
Introduction • Aetiology is not definitely known. Herpes simplex virus and herpes zoster are suspected. • Pathologically, oedema and swelling of the

Aetiology • Herpes zoster is the result of reactivation of varicella zoster virus (VZV) lying dormant in the dorsal root ganglion following chicken p
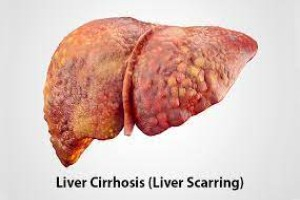
Aetiology of cirrhosis • Alcoholic cirrhosis • Post-necrotic cirrhosis or post-viral cirrhosis • Hepatitis B • Hepatitis C • Delta hepatitis (hepatiti
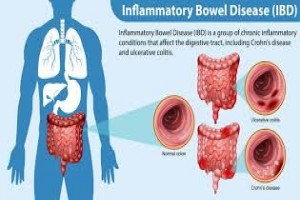
• Inflammatory bowel diseases are chronic inflammatory disorders of gastrointestinal tract characterised by a relapsing and remitting course.
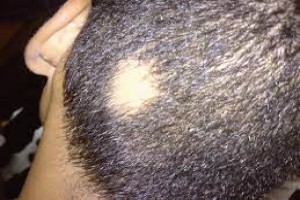
Introduction Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results
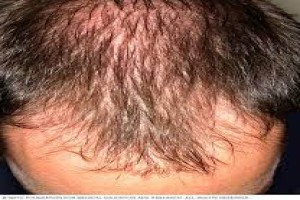
Introduction Hair loss (alopecia) can affect just your scalp or your entire body, and it can be temporary or permanent. It can be the result of hered

Introduction • Depressive disorders are characterised by persistent low mood, loss of interest and enjoyment and reduced energy. They often impair da
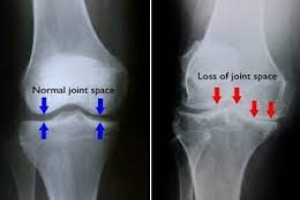
Osteoarthrosis is a degenerative condition of the joints. As there is no inflammatory process, the earlier terminology of osteoarthritis is no longer
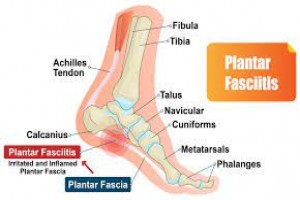
Pain in the heel is one of the common presenting complaints in young adults or middle aged persons. It can also occur in adolescents. The causes of su
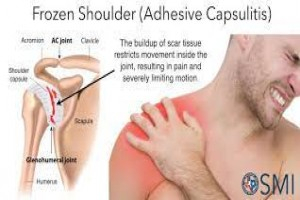
Periarthritis is a condition characterised by in and progressive limitation of some movements of the shoulder joint occurring in the elderly. The pat
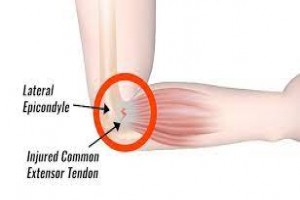
Tennis elbow is an inflammatory condition of the common extensor origin over the lateral epicondyle. This condition does not affect tennis players onl

Ganglion is a cystic swelling in the dorsum of the wrist, It can occur in the volar aspect also. In the dorsum, it consists of synovial protrusion fro
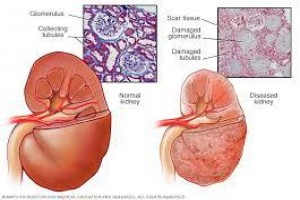
• Chronic renal failure (CRF) is defined as irreversible deterioration in renal function over 3 months with GFR <15/minute/1.73 m2 Causes • Primary

Incidence Tuberculosis of the spine forms 50-60 percent of the total incidence of skeletal tuberculosis. It is a disease of childhood and adolescence,

This is generalised inflammation of the faucial tonsils and is usually caused by haemolytic streptococci. It can occur at any age, but more common in
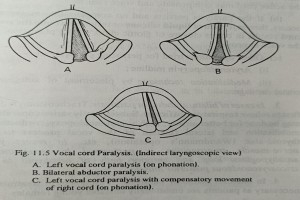
MOTOR PARALYSIS OF THE VOCAL CORDS Vocal cord paralysis may be- (A) Unilateral (a) Right; (b) Left. (B) Bilateral (a) Abductor (b) Adductor (c)

TRIGGER FINGER Trigger finger is a condition of obstruction in the free movement of the finger, with sudden release on extension. This is common in t
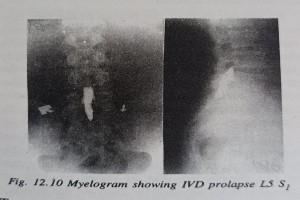
• Lumbago is acute low backache. • Sciatica is the neuralgic pain that starts in the back and radiates along the posterior aspect of lower limb to he
.jpeg)
Allergy is an abnormal response of the tissues to certain material, often a protein, which is called allergen This reaction results in the formation o

Introduction • Fatty liver indicates presence of excess fat in the liver. Causes of Fatty Liver Alcohol Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
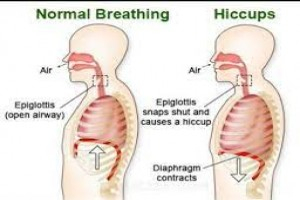
Introduction • Hiccough is a phenomenon resulting from sudden spasmodic involuntary contraction of the diaphragm with the glottis remaining closed.

Introduction • Osteoporosis is characterised by a reduction in the mass of bone per unit volume (osteopenia) to a level below that required for adequ

Anxiety states • Panic disorder • Generalised anxiety disorder • Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) Phobic disorders • Agoraphobia

• Previously grouped under anxiety disorders. • Obsessions are persistent intrusive thoughts. Compulsions are intrusive behaviours. Attempts made to

• Schizophrenia is a group of disorders characterised by perturbations in language, perception, cognition and behaviour. Aetiology • A number of fac

Contents of Cigarette Smoke • More than 4000 substances in cigarette smoke. Mainly, • Carcinogens- Tar • Co-carcinogens-Phenols • Addicting agent-
.jpeg)
• Adult polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is an autosomal dominant disorder. The cortex and medulla of both kidneys are usually filled with thin-walled
.jpeg)
• CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for >3 months, with implications for health. Progression • Major outcomes
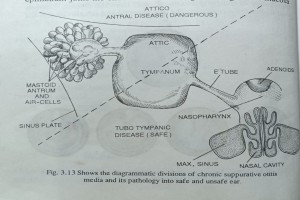
The condition is defined as a long standing chronic suppuration of the middle ear cleft and its muco-periosteal lining resulting in discharging ear an
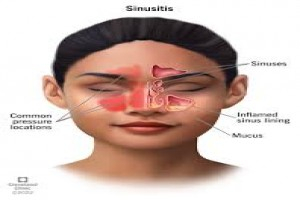
Definition This is chronic inflammatory process affecting the mucosa of various groups of paranasal sinuses. Aetiology 1. Follows repeated attacks

Definition Dilated plexus of superior haemorrhoidal veins, in relation to anal canal. Classification-aetiological I. Primary/Idiopathic haemorrhoid
.jpeg)
There are 2 theories to explain BPH. I. Hormonal theory • It has been compared to fibroadenosis in female patients. • As the age advances, the leve

Introduction Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. The unde

There is hypertrophy of mature fibroblasts in hypertrophic scar. Blood vessels are minimal in this condition. TYPES OF SCAR • Atrophic • Hypertrophic

It is a benign tumour in which the epithelial cells are arranged in a fibrous stroma. It is an AND (Aberration of Normal Development) of a single lobu

RENAL STONES Aetiopathogenesis 1. Infection: Organisms such as Proteus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella produce recurrent UTI. These organisms produce urea,


Abnormal communication between anal canal and rectum with exterior (perianal skin) is called as fistula in ano. Even though multiple openings are seen

Definition Longitudinal tear in the lower end of anal canal results in fissure in ano. It is the most painful condition affecting the anal region. Co

ALOPECIA AREATA This non-scarring condition appears as sharply defined non-inflamed bald patches, usually on the scalp. During the active stage of ha